Here are the top 30 Korean companies and their 2019 financial status.
This article gives you an inside look into what Koreans think about them.

Quick Summary
- Jaebeol means conglomerate, but refers to a family that owns and controls a big company with numerous diversified affiliates.
- The biggest Korean companies are Samsung, Hyundai, SK and LG.
1. Samsung (삼성)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 216,180,920,000,000 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 38,310,673,000,000 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 177,870,247,000,000 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 154,772,859,000,000 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 15,353,323,000,000 KRW |
Most Koreans are very proud of Samsung.
So much that they sometimes call Korea the “Republic of Samsung”.
Founded by Lee Byung-chul, it’s been a family business with Chairman Lee Kun-hee and Vice Chairman Lee Jae-yong.
Recently, Vice Chairman Lee Jae-yong held a press conference and apologized for non-compliance regarding ongoing trials.
What people paid most attention to was him announcing that his children would not succeed him (he has a 20 year-old son and a 16 year-old daughter).
Only time will tell whether Samsung will be managed by the 4th generation or not.
2. Hyundai Motor Company (현대자동차)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 74,157,219,000,000 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 20,238,210,000,000 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 53,919,009,000,000 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 49,155,693,000,000 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 2,832,289,000,000 KRW |
Is Hyundai a Japanese company? No, it’s Korean.
It’s a conglomerate in Korea run by the Chung family.
Chairman Chung Mong-koo succeeded Chung Ju-yung, who started from nothing and became one of the richest men in Korea.
Ulsan is the base of the multinational Hyundai Group, and Koreans nicknamed it the “Republic of Hyundai” or “Hyundai Metropolitan City”.
It’s considered a good place to work as they pay a high salary.
3. SK Group (에스케이)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 22,535,086,000,000 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 9,132,524,000,000 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 13,402,562,000,000 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 3,245,516,000,000 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 1,420,543,000,000 KRW |
SK is the third largest conglomerate in Korea.
Despite what some people think, SK stands for Sunkyong, not South Korea.
Started as Sunkyong Textile in 1953, the cornerstone of this group is energy & chemicals.
SK Group also owns the largest mobile service provider, SK Telecom, which Koreans consider the most reliable.
It has a somewhat positive reputation in Korea as it doesn’t do anything exceptionally well or poorly.
4. LG (엘지)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 9,577,961,000,000 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 251,216,000,000 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 9,326,745,000,000 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 874,672,000,000 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 581,161,000,000 KRW |
Formaly Goldstar, LG is a Korean conglomerate run by the Koo family.
Followed by founder Koo In-hwoi, former Chairman Koo Ja–kyung and Koo Bon-moo, now Koo Kwang-mo runs the group.
LG is also known for smooth successions without bloody battles between family members, thanks to its strict management training.
Its tagline is “Life’s Good“.
LG is especially famous among netizens.
The reason being, LG makes good products, but their marketing team doesn’t always get the word out, so netizens promote LG products for them.
5. Lotte (롯데)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 7,796,179,617,620 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 2,395,666,359,495 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 5,400,513,258,125 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | N/A |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | N/A |
A conglomerate with controversy over its nationality (due to Korea’s history as a colony of Japan).
It’s the only company headquartered in Japan among the top 10 Korean conglomerates.
As you can imagine, Koreans tend to have mixed feelings about this.
Their marketing team seems to be doing its job, because most Japanese people consider it a domestic company.
Lotte was founded by Shin Kyuk-ho, a Korean Japanese person, in 1948.
Then, he expanded his business to Korea with Lotte Confectionery in 1967.
Now, the second son of Shin Kyuk-ho, Shin Dong-bin, runs the group.
Shin Kyuk-ho used to manage the conglomerate by spending odd numbered months in Korea and even months in Japan.
His legacy was to build a 123-floor building, Lotte World Tower, which Koreans often call the “Tower of Sauron”.
6. POSCO (포스코)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 55,710,766,417,120 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 10,096,581,285,877 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 45,614,185,131,243 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 30,373,510,738,515 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 1,175,712,402,299 KRW |
Launched in 1968 with the mission of national industrialization.
It was the first integrated steel mill in Korea.
Posco has grown to produce 41 million tons of crude steel a year.
It’s also a global business with production and sales in 53 countries.
Their reputation is pretty solid in Korea.
Parents would be proud if their children work there.
7. Hanwha (한화)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 7,931,295,000,000 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 4,507,346,000,000 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 3,423,949,000,000 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 4,433,163,000,000 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 100,270,000,000 KRW |
Founder Kim Chong-hee was nicknamed “Dynamite Kim” by the US military for his hot temper during the Korean War.
And things haven’t changed much since.
One example of him being overly passionate was:
When a Japanese student attacked a Korean student while attending high school, Kim Chong-hee beat the Japanese student and got expelled from school.
Kim Chong-hee suddenly died at the age of 58 in 1981 with no successor planned.
There was a dispute between the brothers Kim Seung-yeon and Kim Ho-yeon.
The first son Kim Seung-yeon took over at the age of 29.
But the dispute went on for ten years and ended with Kim Ho-yeon taking Binggrae.
Kim Seung-yeon has 3 sons.
His first son is currently the vice president of Hanwha Q Cells and considered to be the third generation successor.
Unlike his gangster father, addict brother, and other street fighter brother, he’s never caused a problem.
Despite the fact that they own the 63 Building, formerly the tallest in Korea, they continue to maintain their gangster image.
8. GS (지에스)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 6,172,968,000,000 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 758,728,000,000 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 5,414,240,000,000 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 365,336,000,000 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 277,528,000,000 KRW |
GS Group is a Korean conglomerate.
It’s the 8th largest conglomerate in Korea.
GS Holdings was incorporated in 2004 and officially split from LG Group in 2005.
The Koo family has full control over LG Group and the Huh family runs GS Holdings.
GS has a relatively clean image among Koreans.
Their home shopping network is very popular.
They even have their own chain of convenience stores.
9. NongHyup (농협)
NongHyup became one of the top 10 conglomerate groups in 2010.
NFCF (National Agricultural Cooperative Federation) was established with a merger of agricultural cooperatives and the agricultural bank in 1961.
In the decades since, NACF has played an important role in the growth of the Korean economy.
In 2012, NACF started separate operations for its NongHyup Financial and NongHyup Agri-business groups.
NongHyup has a larger presence outside of Seoul given its agricultural roots.
Most people who live away from the capital do their banking with them.
10. Hyundai Heavy Industries (현대중공업)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 8,583,906,445,000 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 2,741,696,853,000 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 5,842,209,592,000 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 492,651,093,000 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 590,858,298,000 KRW |
Hyundai is so big, it made this list twice.
Hyundai Heavy Industries is one of the largest shipbuilding companies in the world.
Headquartered in Ulsan, Hyundai Heavy Industries was founded by Chung Ju-yung in 1972.
Its 4 core business divisions are Shipbuilding, Offshore & Engineering, Industrial Plant & Engineering, and Engine & Machinery.
11. Shinsegae (신세계)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 7,265,903,910,527 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 3,494,702,199,945 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 3,771,201,710,582 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 1,557,606,954,646 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 705,956,104,999 KRW |
12. KT (케이티)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 27,733,854,000,000 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 14,837,153,000,000 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 12,896,701,000,000 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 18,204,751,000,000 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 431,828,000,000 KRW |
13. Hanjin Group (한진)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 1,913,421,079,849 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 373,030,693,449 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 1,540,390,386,400 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | N/A |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 32,069,046,829 KRW |
14. CJ (씨제이)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 2,311,282,516,146 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 2,047,886,723,143 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 263,395,793,003 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 1,046,370,346,744 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | -66,062,360,898 KRW |
15. Doosan (두산)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 11,360,877,605,101 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 7,920,170,221,035 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 3,440,707,384,066 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 3,708,635,207,378 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | -495,190,677,202 KRW |

16. Booyoung (부영)
17. LS (엘에스)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 287,961,695,936 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 12,493,520,970 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 275,468,174,966 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | N/A |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 6,079,714,496 KRW |
18. Daelim (대림)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 10,072,030,499,443 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 4,625,408,469,816 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 5,446,622,029,627 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 7,347,747,862,631 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 396,878,717,263 KRW |
19. Mirae Asset Financial Group (미래에셋)
20. S-Oil (에쓰-오일)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 16,455,433,000,000 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 9,969,313,000,000 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 6,486,120,000,000 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 24,393,980,000,000 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 62,602,000,000 KRW |
21. Hyundai Department Store (현대백화점)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 5,795,560,155,000 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 1,963,854,413,000 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 3,831,705,742,000 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 1,385,243,797,000 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 195,656,742,000 KRW |
22. Hyosung (효성)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 3,186,012,395,511 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 2,242,082,228,246 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 943,930,167,265 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 3,110,979,030,962 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 11,919,974,352 KRW |
23. Korea Investment Holdings (한국투자금융지주)
24. DSME (대우조선해양)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 11,067,648,301,949 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 7,436,139,441,145 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 3,631,508,860,804 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 8,317,581,776,350 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | -57,722,248,994 KRW |
25. Young Poong (영풍)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 2,282,953,196,769 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 462,704,604,322 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 1,820,248,592,447 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 1,347,979,587,535 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 76,098,143,168 KRW |
26. HARIM Co., Ltd. (하림)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 1,614,029,486,351 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 507,805,818,077 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 1,106,223,668,274 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | N/A |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 1,478,669,797 KRW |
27. Kyobo Life Insurance (교보생명보험)
28. Kumho Asiana Group (금호아시아나)
29. Korea Tobacco & Ginseng Corporation (KT&G) (케이티앤지)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 9,112,777,639,505 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 1,332,693,987,094 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 7,780,083,652,411 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 2,942,618,858,461 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 891,380,827,802 KRW |
30. KOLON Group (코오롱)
| Total Assets (자산총계) | 1,272,530,111,868 KRW |
| Total Liabilities (부채총계) | 772,185,761,350 KRW |
| Total Shareholder Equity (자본총계) | 500,344,350,518 KRW |
| Sales Revenue (매출액) | 60,462,264,683 KRW |
| Net Profit (당기순이익) | 9,146,518,952 KRW |
The closest word to “Jaebeol” in English would be conglomerate, but there are a few differences.
Like conglomerates, Jaebeol control numerous diversified affiliates, but their authority over them exceeds legal means.
Most are owned and controlled by families.
These families are similar to royal bloodlines with arranged marriages and successions.
This also means the eldest male often runs the show, regardless of merit.
They’re also linked together financially by marriage and loans.
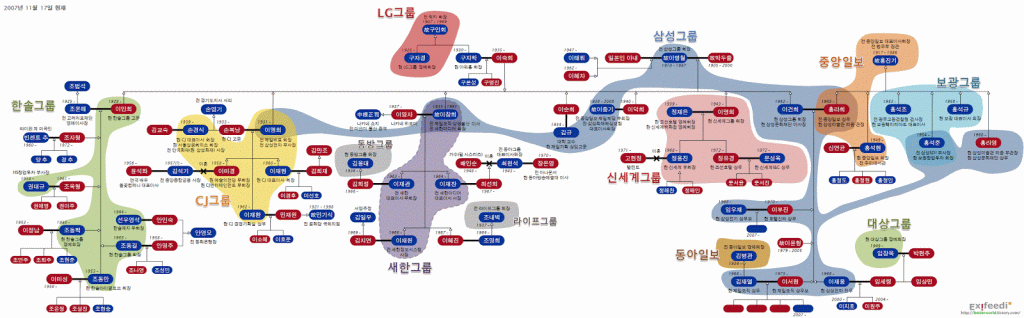
Jaebeol have influence in politics and government as well.
In order to do business in Korea, it’s important to be aware of them as competitors.
The top Korean companies are massive, and go all out when it comes to expansion.
They take “cradle to grave” literally and provide everything from childbirth at their hospitals to funeral services at their funeral homes.
Jaebeol have been both a blessing and curse to South Korea.
Conclusion
South Korean conglomerates carry a lot of weight.
In Korea, we take for granted how much they affect our daily lives. I didn’t realize how much they controlled the Korean economy until I went overseas.
It’s possible for independent businesses and startups to be successful in Korea, provided they have a strong competitive advantage that cannot be replicated.
Thank you for reading.



